Habener, Mosjov and Knudsen win the Lasker award
The current GLP1 receptor agonist boom was made possible by the work of Joel Habener, Lotte Bjerre Knudsen, and Svetlana Mojsov.


To surprisingly little fanfare, Joel Habener, Lotte Bjerre Knudsen, and Svetlana Mojsov have won the Lasker award – formally known as the "Lasker-Debakey Clinical Medical Research Award".
Outside of the Nobel prize, this is one of the most coveted awards in medical research, earned by pioneers who have truly moved the dial for humanity as a whole, and medicine.

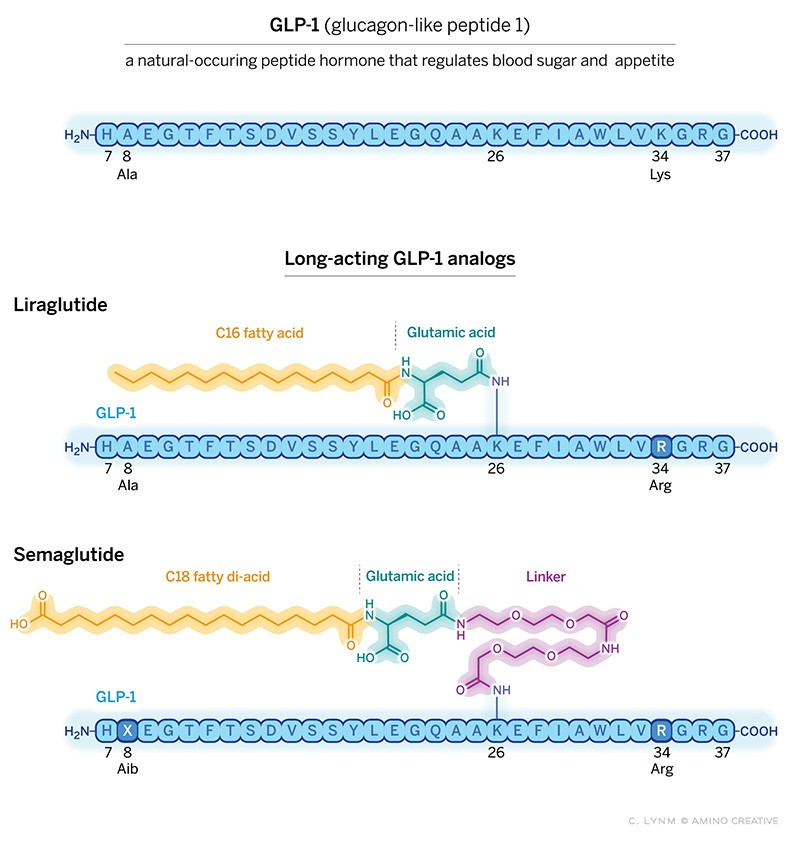
You can go back to work as early as 1993 to see Joel Habener's involvement with GLP-1 research:
Along with patent filings back in 1996:

Who has won the Lasker award in the past?
The Wikipedia is the best place to find a definitive listing of the recipients of the Lasker award (some posthumously), but there are a couple worth mentioning right from the outset of the award being given.
John Friend Mahoney (Blood group system, transfusions)

John was one of the people to receive the Lasker award in 1947 along with Karl Landsteiner (posthumously), Alexander S. Wiener, and Philip Levine. All three scientists have incredibly work under their belt.
Thomas Francis Jr (Influenza Vaccine)

Thomas was awarded the Lasker award in 1947 (the second year it was awarded)
Who's won the Lasker award recently?
There are many incredibly impressive winners of the Lasker award recently as well, but here we highlight a few:
Katalin Karikó

Katalin was awarded the Lasker prize for her instrumental work in enabling mRNA vaccines – using mRNA for protein placement. She was awarded the Lasker award in 2021.
Denis Lo Yuk-ming (non-invasive Prenatal testing, Liquid biopsy)

Denis was awarded the Lasker prize in 2022 for his extensive work with prenatal testing and detection/biopsy.
James Fujimoto (OCT imaging)

James (along with David Huang and Eric A. Swanson) were recognized for creating Optical coherence tomography (OCT) imaging – a technique that creates stunningly detailed and multi-layered scans of tissue, at micrometer resolution.
You can read much more about the prize on Wikipedia: